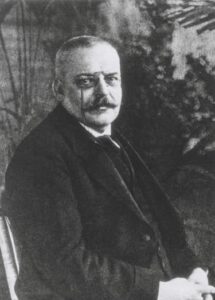
by National Institute on Aging
Alzheimer’s disease is a brain disorder that slowly destroys memory and thinking skills, and, eventually, the ability to carry out the simplest tasks. In most people with Alzheimer’s, symptoms first appear later in life. Estimates vary, but experts suggest that more than 6 million Americans, most of them age 65 or older, may have dementia caused by Alzheimer’s.
Alzheimer’s disease is currently ranked as the sixth leading cause of death in the United States, but recent estimates indicate the disorder may rank third, just behind heart disease and cancer, as a cause of death for older people.
Alzheimer’s is the most common cause of dementia among older adults. Dementia is the loss of cognitive functioning — thinking, remembering, and reasoning — and behavioral abilities to such an extent that it interferes with a person’s daily life and activities. Dementia ranges in severity from the mildest stage, when it is just beginning to affect a person’s functioning, to the most severe stage, when the person must depend completely on others for help with basic activities of daily living.
The causes of dementia can vary, depending on the types of brain changes that may be taking place. Other dementias include Lewy body dementia, frontotemporal disorders, and vascular dementia. It is common for people to have mixed dementia — a combination of two or more types of dementia. For example, some people have both Alzheimer’s disease and vascular dementia.
Alzheimer’s disease is named after Dr. Alois Alzheimer. In 1906, Dr. Alzheimer noticed changes in the brain tissue of a woman who had died of an unusual mental illness. Her symptoms included memory loss, language problems, and unpredictable behavior. After she died, he examined her brain and found many abnormal clumps (now called amyloid plaques) and tangled bundles of fibers (now called neurofibrillary, or tau, tangles).
These plaques and tangles in the brain are still considered some of the main features of Alzheimer’s disease. Another feature is the loss of connections between neurons in the brain. Neurons transmit messages between different parts of the brain, and from the brain to muscles and organs in the body.
How is Alzheimer’s disease diagnosed? Doctors use several methods and tools to help determine whether a person who is having memory problems has Alzheimer’s disease.
To diagnose Alzheimer’s, doctors may:
Ask the person and a family member or friend questions about overall health, use of prescription and over-the-counter medicines, diet, past medical problems, ability to carry out daily activities, and changes in behavior and personality.
Conduct tests of memory, problem solving, attention, counting, and language.
Carry out standard medical tests, such as blood and urine tests, to identify other possible causes of the problem.
Perform brain scans, such as computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), or positron emission tomography (PET), to support an Alzheimer’s diagnosis or to rule out other possible causes for symptoms.
These tests may be repeated to give doctors information about how the person’s memory and other cognitive functions are changing over time.
